Development of SCB-PPS, a new addition to the lineup of Smart Cellular Board low dielectric materials
- Requirements for the materials used in base stations are becoming more sophisticated because of increased telecommunications traffic and advances in 5G/Beyond 5G
- Using PPS plastic, we developed SCB-PPS with low dielectric, lightweight, high heat resistance and flame retardancy
- Through material development leveraging our original technology, we will contribute to realizing a Beyond 5G/6G society
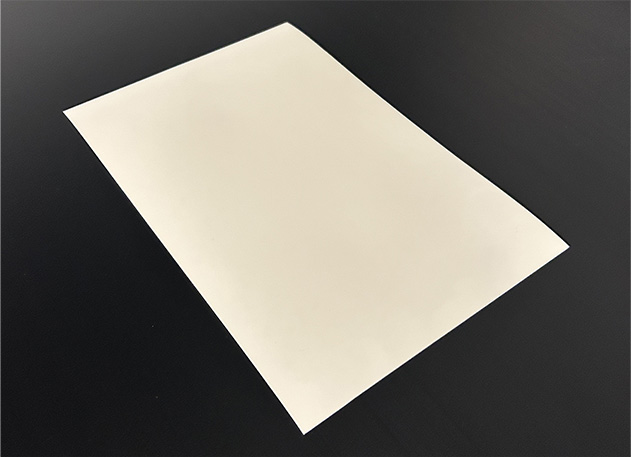
Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd. (Head office: 2-6-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo; President: Hideya Moridaira) developed SCB-PPS as a new addition to the lineup of Smart Cellular Board (hereinafter, SCB) low dielectric materials. This new material possesses high heat resistance and flame retardancy in addition to the traditional strengths of SCB including low dielectric constant (Dk), dissipation factor (Df) and lightweight.
Background
In recent years, the traffic through telecommunications networks is growing worldwide following the increased use of smartphones, cloud computing, video streaming and generative AI. Going forward, this traffic is forecast to rapidly grow further in response to advances in 5G/Beyond 5G, accelerated installation of telecommunications infrastructure in rural and mountain regions and new uses including autonomous driving. Given these trends, the demand for data centers is increasing around the world. The number of base stations that send and receive data are also increasing, and the requirements for material performance are becoming more advanced to include improved device performance and safety along with the typical installation and maintenance requirements.
Details
The new SCB-PPS has been developed using PPS (polyphenylene sulfide), a super engineering plastic with low dielectric constant (Dk) and dissipation factor (Df), as well as heat resistance, flame retardancy, mechanical strength and chemical resistance.
SCB-PPS has heat resistance and flame retardancy on the same level as the solder heat resistance inherently possessed by solid PPS, while the dielectric constant (Dk) and dissipation factor (Df) have been reduced by about 40% and density has been reduced by about 70% compared to solid PPS. With these properties, SCB-PPS can be safely used near high output devices, including the base station radome and antenna circuit board and in hot environments such as outdoor locations. In addition, this material will contribute to further reducing dielectric loss at high frequencies used for 5G and 6G telecommunications(Note) and the structural load of base stations, which often face installation restrictions. Also, because this new material can resist high temperatures during processing, it should be possible to use it in applications including flexible printed circuit boards. We plan to start shipping samples of SCB-PPS in August 2025.
Going forward, we will continue to leverage our original technology to develop materials such as SCB that respond to customer requirements and contribute to the realization of a Beyond 5G/6G society.
| Item | Unit | Physical property | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | g/cm3 | 0.4 | |
| Melting point | ℃ | 275 | |
| Tensile strength | MPa | MD | 22 |
| TD | 15 | ||
| Tensile elongation | % | MD | 32 |
| TD | 30 | ||
| Dielectric constant Dk@2.45GHz | - | 1.6 | |
| Dissipation factor Df@2.45GHz | - | 0.0015 | |
| UL-94 flame retardancy (Version 5) | - | V-0 | |
| Thickness | mm | 0.8 | |
* Table does not indicate specification values. Because the material is still under development, the target values may change.
(Note) Dielectric loss=k × f × √Dk × Df (k: Constant, f: Frequency, Dk: Dielectric constant, Df: Dissipation factor)
Low dielectric foam material Smart Cellular Board(SCB)
SCB is a cellular foamed, board type low dielectric material made using original batch foaming technology. It possesses low dielectric constant (Dk) and dissipation factor (Df) and solves issues including reduced radio wave permeability and increased transmission loss resulting the use of higher frequencies. Moreover, it is lightweight and has high heat resistance, and it contributes to smaller base station and data center devices and increased installation density.

Related news release
Furukawa Electric Group’s efforts towards the SDGs
Based on the “Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)” adopted by the United Nations, Furukawa Electric Group has formulated the “Furukawa Electric Group Vision 2030” which sets the year 2030 as its target and is advancing efforts with the aim to “Build a sustainable world and make people’s life safe, peaceful and rewarding, Furukawa Electric Group will create solutions for the new generation of global infrastructure combining information, energy and mobility.” Toward the achievement of our Vision 2030, we will take open, agile, and innovative approaches to promote ESG management that aims to increase corporate value over the medium to long term and will contribute to the achievement of the SDGs.

 Share
Share Tweet
Tweet Share
Share